Exploring the Transformative Potential of Stem Cells in Medicine
Stem cells are the building blocks of the body, capable of dividing and renewing themselves for long periods. Unlike other cells, they have the remarkable potential to develop into many different cell types in the body during early life and growth. In many tissues, they serve as a sort of internal repair system, dividing without limit to replenish other cells as long as the person or animal is still alive.
What Are Stem Cells?
what is stem cell? Stem cells are distinguished from other cell types by important characteristics.
| Characteristic | Description | Example Organs |
|---|---|---|
| Replication | Can replicate themselves over extended periods, even after inactivity | Gut, bone marrow |
| Differentiation | Can transform into specialized cells with specific functions | Can become blood cells, skin cells, etc. |
| Regular Repair | Actively divide to replace damaged tissue | Gut, bone marrow |
| Conditional Repair | Primarily divide in response to injury or specific signals | Pancreas, heart |

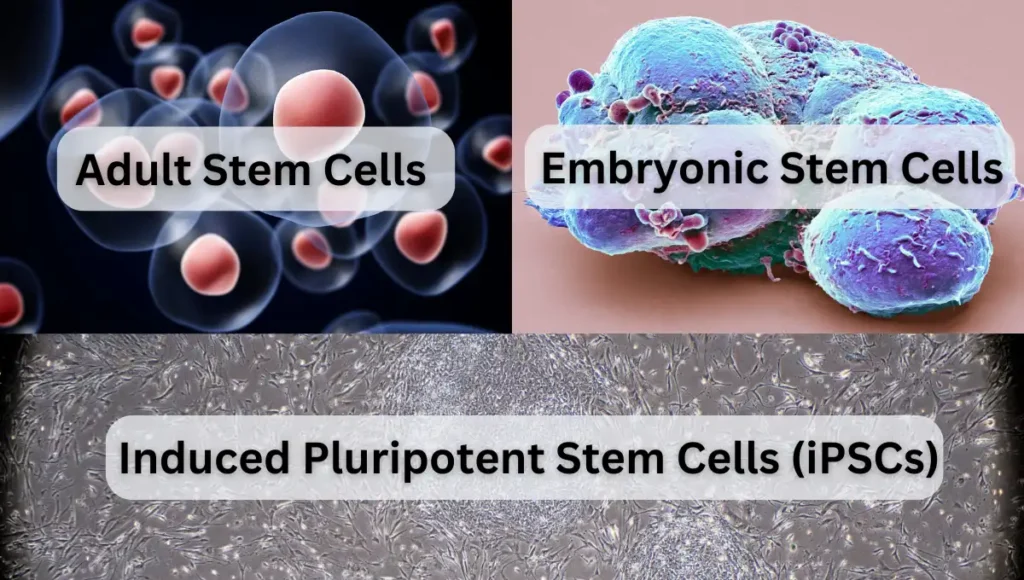
Types of Stem Cells and Their Sources
Embryonic Stem Cells
These cells are derived from embryos that are three to five days old. At this stage, an embryo is called a blastocyst and has about 150 cells. Embryonic stem cells are pluripotent, meaning they can turn into more than 200 different cell types in the body.
Adult Stem Cells
Found in small numbers in most adult tissues, such as bone marrow or fat, adult stem cells are limited in their ability to differentiate but are capable of generating replacements for some types of cells that are lost through normal wear and tear, injury, or disease.
Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells (iPSCs)
Scientists have successfully transformed regular adult cells into stem cells using genetic reprogramming. By altering the genes in the adult cells, they can reprogram the cells to act similarly to embryonic stem cells. This breakthrough has provided new ways to understand disease and develop treatments.
Stem Cells: The Power to Heal, Repair, and Discover
The potential of stem cells spans several fields of health and medical research. From regenerative medicine to understanding the complexities of cancer, the applications are vast:
Regenerative Medicine
This involves the generation of cells, tissues, or organs to replace or establish normal function. Researchers are already using stem cell therapy in the transplantation of bone marrow, which can help treat conditions such as leukemia and lymphoma.
Organ Repair and Replacement
As research progresses, scientists anticipate being able to use technologies like stem cells to regenerate damaged organs, potentially reducing the need for organ transplants and the risk of rejection.
Disease Modelling and Treatment Development
Stem cells can be used to create cells and tissues for medical therapies. Imagine testing drugs on a cardiac muscle cell made from a patient’s own skin cells, revolutionizing personalized medicine.

Ethical Considerations and Future Directions
Despite their potential, stem cell research raises ethical concerns, particularly with embryonic stem cells. This controversy primarily relates to the methods through which the human embryos are created and used. Researchers are eager to explore alternatives like iPSCs to bypass these ethical concerns.
Moreover, the technology’s applications in cloning and genetic modification continue to invoke ethical and practical debates globally. As we navigate these debates, the integration of strict regulations and ethical guidelines will be essential for advancing research and application.
In conclusion, stem cells hold the promise to revolutionize medicine, offering new treatments and insights into human health and disease. However, as with any powerful technology, balancing innovation with ethical considerations will be crucial to its success.










Pingback: Foods That Generate Stem Cells - IRM Hospital
Pingback: IV Stem Cell Therapy at IRM Hospital, Islamabad: Pioneering Regenerative Medicine - IRM Hospital
Pingback: Future of Stem Cell Therapy in Pakistan - IRM Hospital
Pingback: Stem Cell vs Bone Marrow Transplant: Understanding the Differences
Pingback: Ultimate Stem Cell Therapy Comparison: Which is Best in 2024
Pingback: Collagen - IRM Hospital
Pingback: Anti-apoptosis: Exploring the Mechanisms of Cell Survival and Therapeutic Implications - IRM Hospital
Pingback: Combatting Chronic Inflammation: A Comprehensive Guide - IRM Hospital
Pingback: Introduction to Immunomodulation - IRM Hospital
Pingback: Paracrine Signalling Understanding Cellular Communication