Stem Cell Transplant vs Bone Marrow Transplant: Understanding the Differences and Advancements in Regenerative Medicine
In regenerative medicine, stem and bone marrow transplants are critical therapies for various life-threatening conditions. These procedures, pivotal in treating diseases like leukemia, lymphoma, and multiple myeloma, have transformed patient outcomes across hematology. This article delves into the nuances of each treatment, comparing their methodologies, applications, and innovations shaping their future.Understanding the Fundamentals of TransplantationBone Marrow Transplant: The Traditional ApproachA bone marrow transplant involves replacing damaged or diseased bone marrow with healthy stem cells. Bone marrow, the soft, fatty tissue inside your bones, produces blood cells from hematopoietic stem cells. The transplant aims to replenish the body’s ability to produce
Stem Cell Therapy Comparison with Other Healing Methods
In the evolving landscape of medical treatments, stem cell therapy comparison emerges as a groundbreaking option, offering new hope and possibilities for patients with various conditions. This article compares stem cell therapy with other healing methods, exploring its unique advantages, applications, and considerations against more traditional and alternative treatments.Understanding Stem Cell TherapyStem cell therapy, or regenerative medicine, involves using stem cells to repair or replace damaged tissues and cells. This innovative approach can treat various health issues, from chronic diseases to acute injuries and degenerative conditions. The foundational science behind stem cell therapy relies on cell differentiation and proliferation, where stem cells transform into
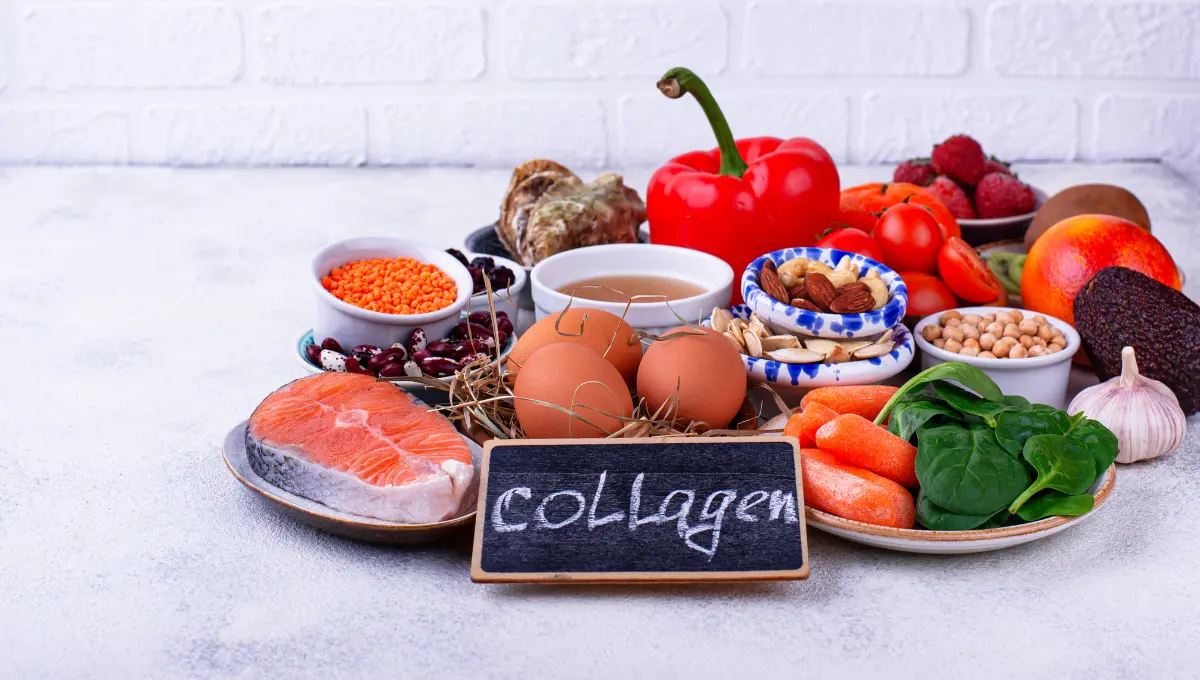
The Main Types of Collagen: What You Need to Know
Collagen is the most abundant protein in the human body, playing a pivotal role in constructing our skin, bones, muscles, tendons, and ligaments. The fascination with collagen has transcended medical boundaries, entering the realms of beauty, nutrition, and general wellness. This article delves deep into the different collagen forms, exploring their sources, benefits, and the numerous applications they find in our daily lives.Understanding the Various Forms of CollagenCollagen is not a singular entity but comes in various forms with unique properties and benefits. Here, we explore the most prevalent types integral to human health and beauty.Type I Collagen: The Bedrock
What is Collagen: The Essential Protein Powering Beauty and Health
Collagen is more than just a buzzword in the beauty and wellness industry; it is a fundamental element that is woven into the very fabric of our biology. This protein is pivotal for maintaining the structural integrity of our skin, bones, and connective tissues. It's not only a cornerstone of health but also a beacon of youthful vitality and longevity.Understanding Collagen and Its ImportanceCollagen is the most abundant protein in the human body, making up about a third of our total protein composition. It forms a scaffold to provide strength and structure, supporting everything from skin elasticity to joint functionality.
Halting Scarring: A Look at Fibrosis Inhibition
Fibrosis is a complex biological process characterized by the excessive accumulation of extracellular matrix components, including collagen, which can lead to the scarring of various tissues and organs.This scarring process interferes with the normal function of the affected organs, making Fibrosis a significant contributor to morbidity and mortality in diseases such as pulmonary Fibrosis, liver cirrhosis, and renal Fibrosis.The inhibition of Fibrosis, therefore, represents a crucial area of medical research, focusing on developing strategies and therapies to prevent or reduce this pathological tissue remodeling.Understanding the Biological Basis of FibrosisAt the heart of Fibrosis is the pathological accumulation of
Angiogenesis: The Vital Process of Blood Vessel Growth and Its Impact on Health
Angiogenesis, the formation of new blood vessels from existing ones, is a cornerstone of human physiology and pathology. This intricate process is pivotal not only in normal body functions such as wound healing and reproduction but also plays a critical role in disease progression, particularly in cancer and ischemic diseases. Understanding angiogenesis provides insights into potential therapeutic targets and diagnostic approaches, making it a vital area of medical research.The Biological Basis of AngiogenesisAt its core, angiogenesis involves the proliferation and migration of endothelial cells, which line the interior surface of blood vessels. These cells respond to various signals, such as
Anti-apoptosis: Exploring the Mechanisms of Cell Survival and Therapeutic Implications
Apoptosis, or programmed cell death, is a crucial biological process that ensures the proper development and functioning of living organisms by eliminating unnecessary or damaged cells.However, the inhibition of apoptosis, also known as anti-apoptosis, plays a pivotal role in various physiological and pathological contexts, particularly in the realm of oncology and neurodegenerative diseases.This article delves into the mechanisms of apoptosis inhibition, explores its biological significance, and discusses the therapeutic potentials and challenges associated with modulating apoptosis pathways.The Biological Basis of Apoptosis InhibitionApoptosis is a highly regulated process that involves a series of molecular events designed to carry out
Reduce Chronic Inflammation: Strategies for Health and Healing
Chronic inflammation is often a silent antagonist lurking behind the scenes of major health disorders. While acute inflammation is a natural and beneficial response of the immune system, chronic inflammation can lead to a myriad of health issues if not managed properly.This comprehensive guide explores effective strategies for managing chronic inflammation through a holistic approach, encompassing dietary adjustments, lifestyle changes, and therapeutic interventions.Understanding Chronic InflammationChronic inflammation is a prolonged, harmful response of the immune system that can affect various parts of the body, manifesting in numerous diseases and conditions.Unlike acute inflammation, which is a short-lived and necessary response
Immunomodulation: Understanding Immune System Regulation
Immunomodulation encompasses a range of strategies to adjust the immune system’s response, either by enhancing its activity to fight infections and cancer cells or by suppressing it to mitigate allergies and autoimmune diseases.This dual role makes immunomodulation a cornerstone in both therapeutic interventions and preventive medicine.Understanding the Immune System’s MachineryThe human immune system is a complex network of cells, tissues, and organs that work in concert to defend against pathogens.Central to this system are T-cells and B-cells, which regulate cellular and humoral immunity, respectively.Depending on the therapeutic needs, immunomodulation often targets these cells to enhance or suppress
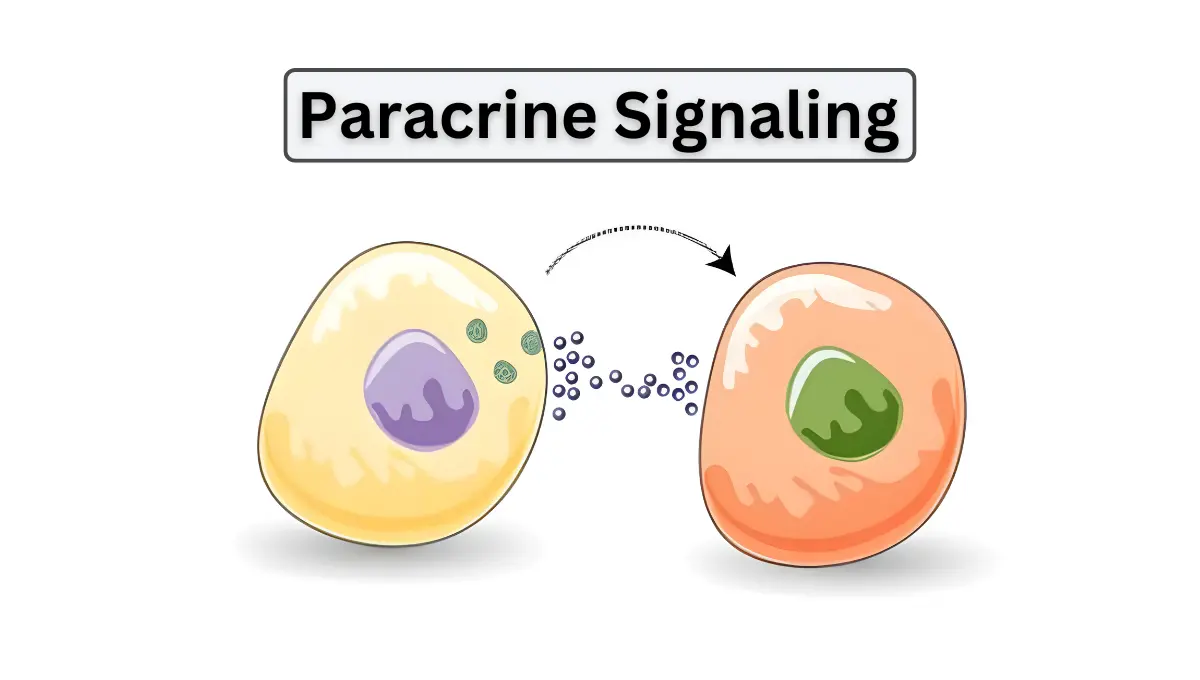
Paracrine Signaling: The Basics of Local Cell Communication
Paracrine signalling is a fundamental aspect of cellular communication that involves the transfer of signals between neighboring cells to regulate a variety of physiological processes.This type of signaling is critical in numerous biological functions, including tissue repair, immune responses, and cellular growth and differentiation.Understanding the Basics of Paracrine CommunicationUnlike endocrine signaling, which involves hormones traveling long distances through the bloodstream, paracrine signals are localized, affecting only cells in the immediate vicinity of the signal-emitting cells.This method of signaling is crucial for fine-tuning cellular responses in a specific tissue environment.The Role of Growth Factors and CytokinesGrowth factors are prominent