Reduce Chronic Inflammation: Strategies for Health and Healing
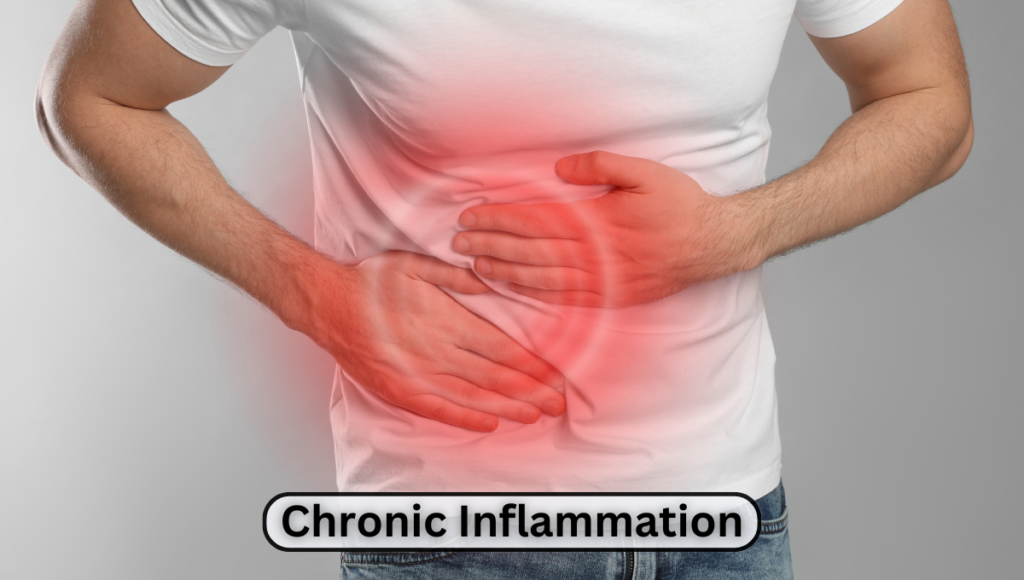
Chronic inflammation is often a silent antagonist lurking behind the scenes of major health disorders. While acute inflammation is a natural and beneficial response of the immune system, chronic inflammation can lead to a myriad of health issues if not managed properly.
This comprehensive guide explores effective strategies for managing chronic inflammation through a holistic approach, encompassing dietary adjustments, lifestyle changes, and therapeutic interventions.
Understanding Chronic Inflammation
Chronic inflammation is a prolonged, harmful response of the immune system that can affect various parts of the body, manifesting in numerous diseases and conditions.
Unlike acute inflammation, which is a short-lived and necessary response to injury or infection, chronic inflammation can persist for months or even years, often without clear symptoms.
This type of inflammation is associated with diseases such as arthritis, heart disease, diabetes, and many autoimmune disorders.
The pathophysiology of inflammation is complex, involving a cascade of cellular events and cytokine releases that can eventually cause tissue damage.
Chronic inflammation often starts silently; it might not show any symptoms until significant damage has occurred, making it imperative to understand and manage early.
Dietary Approaches to Reduce Inflammation
One of the most effective ways to combat chronic inflammation is through dietary adjustments. There are many foods that generate stem cells, which may help in applying a balanced stem cell therapy to treat the condition.
An anti-inflammatory diet focuses on incorporating foods known to reduce inflammatory responses while eliminating those that trigger it.
Exploring the Transformative Potential of Stem Cells in Medicine
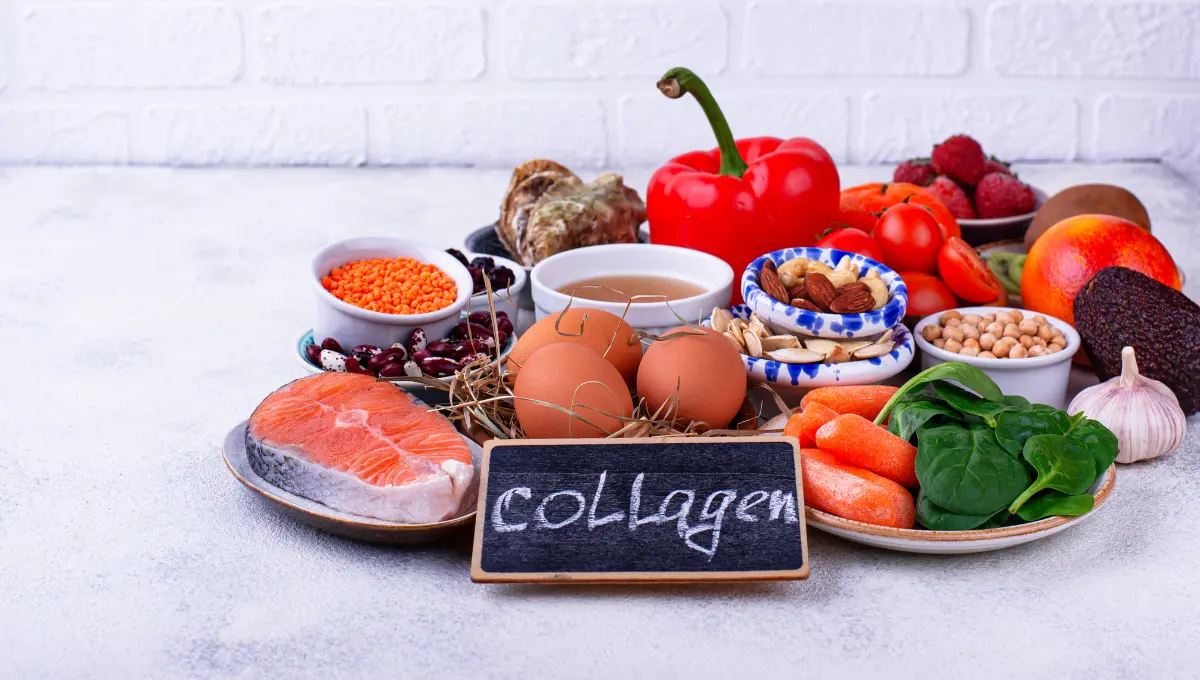
The Anti-Inflammatory Diet: Foods that Fight Inflammation
Foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids, such as salmon, flaxseeds, and walnuts, are known for their ability to reduce inflammation. Spices like turmeric, which contains the active compound curcumin, have been extensively studied for their potent anti-inflammatory properties.
Additionally, adopting a Mediterranean diet, which emphasizes fruits, vegetables, nuts, whole grains, and healthy fats, has been shown to significantly reduce inflammatory markers.
Lifestyle Modifications to Support Anti-Inflammatory Living
Beyond diet, lifestyle plays a crucial role in managing inflammation. Regular exercise, adequate sleep, and stress reduction are pivotal in maintaining optimal health and minimizing inflammation.
Exercise as a Pillar of Inflammatory Control
Engaging in regular physical activity helps to reduce inflammation by releasing anti-inflammatory cytokines and reducing adipose tissue, which is known to produce inflammatory markers.

A consistent exercise regimen, whether it’s aerobic activities like walking or cycling, or strength training, can have profound anti-inflammatory effects.
The Role of Sleep and Stress Management in Inflammation
Adequate sleep is essential for the immune system to function properly. Poor sleep patterns can exacerbate inflammation and weaken the immune response. Similarly, chronic stress triggers the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines.
Techniques such as mindfulness, yoga, and meditation can be effective in reducing stress and, consequently, inflammation.
Advanced Therapeutic Interventions
For individuals with severe or persistent inflammation, medical interventions may be necessary.
This can range from over-the-counter non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) to more targeted biologic therapies designed to interrupt specific inflammatory pathways.
Holistic and Complementary Therapies
Holistic treatments such as acupuncture, massage, and the use of natural anti-inflammatories can complement conventional treatments by providing relief and reducing inflammation without the side effects often associated with traditional medications.
Conclusion
Managing chronic inflammation requires a multifaceted approach. By combining dietary strategies, lifestyle adjustments, and appropriate medical interventions, individuals can effectively manage and reduce the impacts of chronic inflammation on their health.
Through vigilant care and preventive practices, it is possible to lead a healthier and more vibrant life, free from the burdens of inflammation.