Stem Cell Transplant vs Bone Marrow Transplant: Understanding the Differences and Advancements in Regenerative Medicine
In regenerative medicine, stem and bone marrow transplants are critical therapies for various life-threatening conditions. These procedures, pivotal in treating diseases like leukemia, lymphoma, and multiple myeloma, have transformed patient outcomes across hematology. This article delves into the nuances of each treatment, comparing their methodologies, applications, and innovations shaping their future.
Understanding the Fundamentals of Transplantation
Bone Marrow Transplant: The Traditional Approach
A bone marrow transplant involves replacing damaged or diseased bone marrow with healthy stem cells. Bone marrow, the soft, fatty tissue inside your bones, produces blood cells from hematopoietic stem cells. The transplant aims to replenish the body’s ability to produce blood cells and restore the immune system—a crucial step in overcoming hematological malignancies.
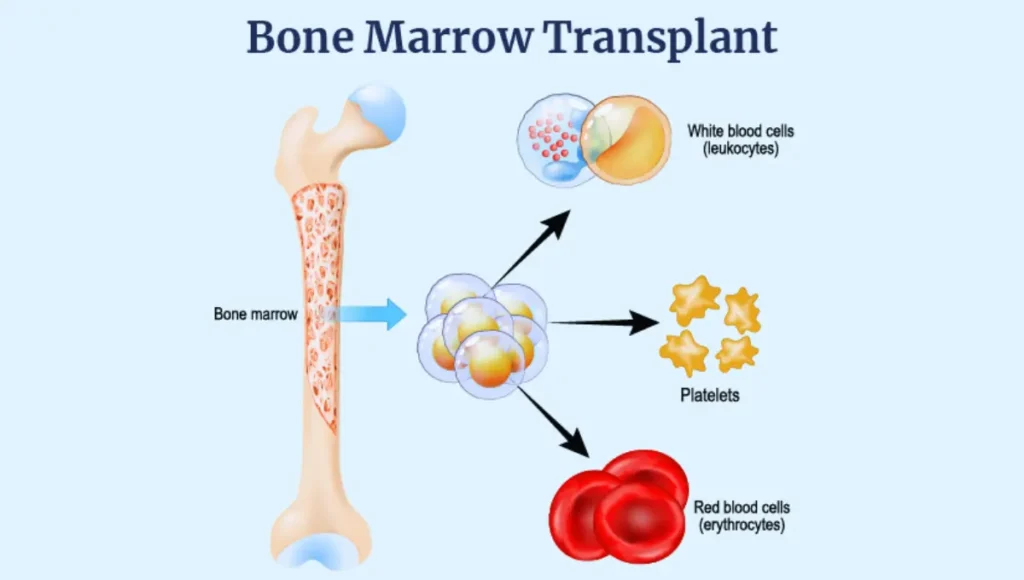
Stem Cell Transplant: The Broad Spectrum Approach
In contrast to traditional marrow grafting, a stem cell transplant can be derived from various sources, including bone marrow, peripheral blood, and cord blood. These transplants are primarily used to regenerate damaged tissues and organs, offering a broader scope of application beyond hematological uses, extending to autoimmune diseases and other conditions.
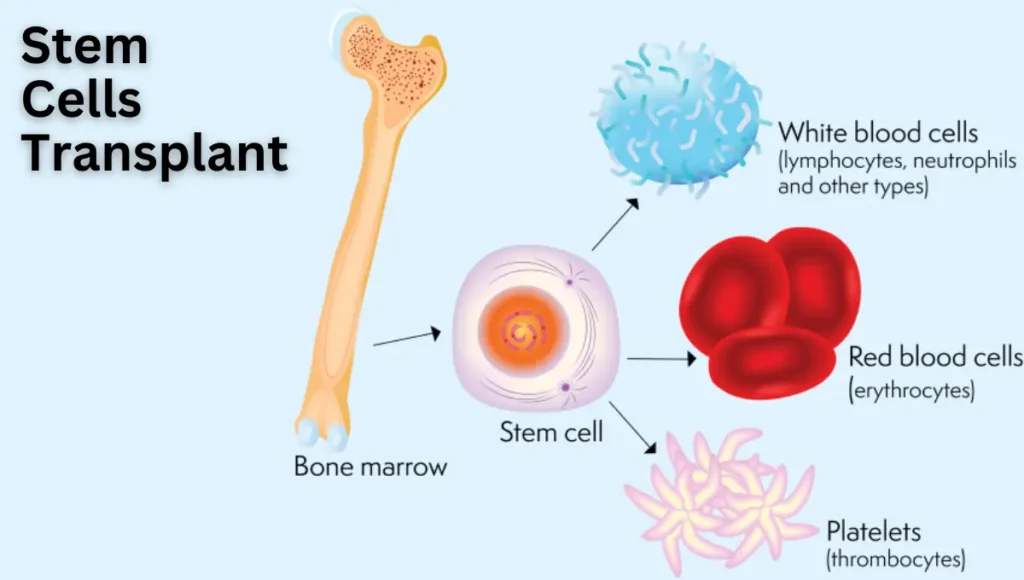
Stem Cell Therapy: Discover the Healing Power of Regenerative Medicine
Types of Transplants: Autologous and Allogeneic
Autologous Transplants: Self-Sourced Cells
In an autologous transplant, patients receive their own stem cells, collected typically from peripheral blood stem cells through apheresis. This type of transplant significantly reduces the risk of graft-versus-host disease (GVHD). It is commonly utilized in situations where the patient’s cells can be a sufficient cure.
Allogeneic Transplants: Donor-Derived Cells
Allogeneic transplants involve stem cells sourced from a donor—a family member, an unrelated donor, or cord blood units. The key to successful allogeneic transplantation lies in the compatibility between donor and recipient, assessed through meticulous genetic testing to minimize the risk of GVHD and optimize engraftment success.
Innovative Advances in Transplant Techniques
In recent years, we have seen remarkable advancements in transplant technologies. Genetic engineering and CRISPR technology have paved the way for gene editing to combat genetic disorders and improve the safety and efficacy of transplants. Furthermore, innovations like immunotherapy are being integrated with transplant protocols to enhance the immune system’s ability to fight cancer and other diseases more effectively.
Challenges and Risks: GVHD and Transplant Rejection
Despite advancements, transplant surgeries carry inherent risks, such as GVHD, where the donor cells attack the recipient’s body, and transplant rejection. Comprehensive post-transplant care, including immunosuppression management and infection prevention, is critical to mitigate these risks and ensure successful patient outcomes.
The Future of Transplant Medicine
The landscape of transplant medicine continues to evolve with ongoing research and clinical trials aimed at enhancing the effectiveness and reducing the risks associated with these life-saving procedures. As biotechnology advances, the potential for treating a wider range of diseases grows, promising a future where stem cell and bone marrow transplants become even more effective and less invasive.

Conclusion
Stem cell and bone marrow transplants represent cornerstone therapies in treating severe and often life-threatening diseases. By understanding the specific applications and advancements in each method, patients and healthcare providers can better navigate the complexities of these treatments and make informed decisions that optimize health outcomes.
Patient Care and Recovery: A Holistic Approach
Post-treatment care is crucial in ensuring the success of a transplant. A holistic approach to recovery, addressing both physical and psychological health, supports a smoother recovery and long-term health.







